Detecting Radiation In Scrap Metal
Many countries, such as India have regulations in place, which require shipments of scrap metal destined to the country to be screened for radioactive materials prior to leaving the port of origin.
The Importance of Screening Scrap Metal for Radiation
ThermoFisher Scientific has a good artilce on their website, which gives a real life case of what happened when a radiation source in scrap metal wasn't identified. You can read this article by clicking on the following link:
Hundreds Were Accidentally Poisoned 35 Years Ago by Rogue Radiation Source
Hand Held Radiation Survey Meters for Scrap Metal Screening
One of the best hand held devices for screening scrap metal is the Thermo Scientific RadEye GN radiation survey meters.
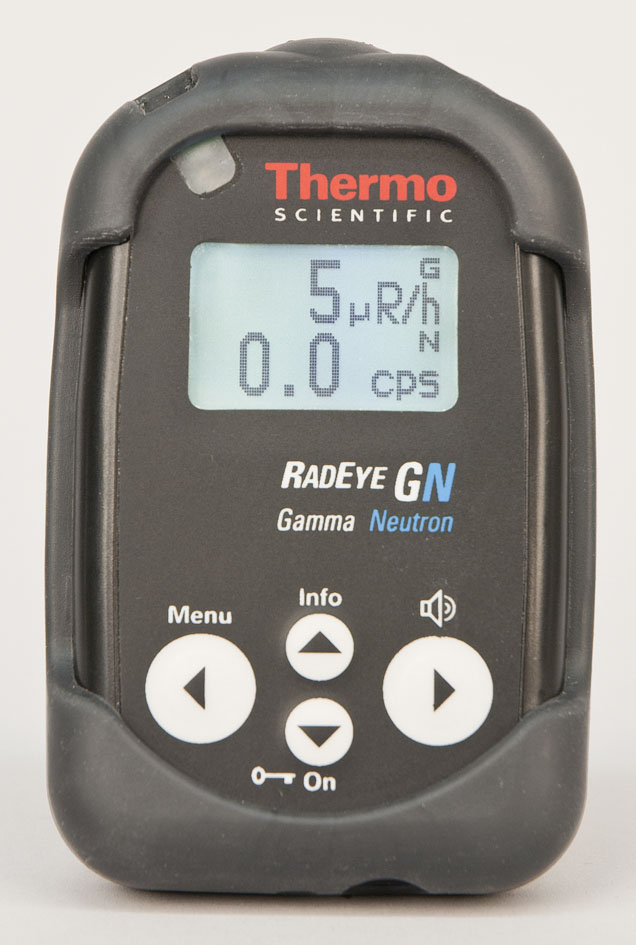
This highly sensitive and rugged measuring instrument is designed to detect and survey gamma and neutron radiation, making it ideal for detecting radiation in security or industrial applications, such as metal recycling.
These small lightweight radiation detectors use NBR technology (Natural Background Rejection) to separate man made and naturally occurring background fluctuations.
Both the Radeye GN and GN+ incorporate a single highly sensitive scintillation detector which is equipped with a miniature photo-multiplier allowing the detection of very low radiation levels of both gamma and neutron radiation.
The RadEye GN uses a conventional Li-6 doped glass material and meets ANSI Standard 42.32 and 42.33 part 1 and IEC 62401. It features both audible and visual alarms to identify whether the alarms are due to gamma or neutron radiation, and whether the radiation source is from higher than usual natural background radiation, or a man-made radiation source.
The RadEye GN can be used with a compact moderator which transforms it into a powerful gamma-neutron search device at minimal cost.
Performance verification can be achieved through using two specific test adaptors containing natural radioactivity that are available through ADM Nuclear Technologies.
The RadEye GN records up to 1600 mean and maximum values of gamma and neutron radiation in its internal data logger.
The key difference between the RadEye GN and GN+ is the count efficiency:
RadEye GN: 1000 cps / µSv/h (Am-241); 110 cps / µSv/h (Cs-137); 65 cps / µSv/h (Co-60)
RadEye GN+: 2000 cps / µSv/h (Am-241); 110 cps / µSv/h (Cs-137); 55 cps / µSv/h (Co-60)
identifying Radiation sources In Large Shipments of Scrap Metal
In recent years several incidents have been reported, where orphan AM-241 sources have been inadvertently included in scrap metal being melted down in the furnaces of a steel plant.
The steel itself remains largely uncontaminated with such radioactive neutrons. Due to its physical properties - most of the AM-241 activity ends up on the slag heap and in dust. This means the cost of clean-up and disposal are significant. As well as the serious inhalation risk to the work force, since the radio toxicity of Am-241 is comparable to Plutonium.
The half-life of AM-421 is 433 years.
One real concern is that the number of incidents where AM-421 has been melted in a furnace may be much higher than thought, as slag is not always monitored for radiation contamination.
Unlike other industrial radiation sources (Co-60, Cs-137, Ir-192, Eu-152) and naturally occurring radioactive materials (NORM), Am-241 predominantly emits low energy gamma radiation. Typically below 100 keV (mainly 59 keV).
The emission rate of penetrating higher energy gamma radiation is very low (in the order of E-5), so that even high activity sources can remain undetected by conventional radiation detection systems that are based on gamma detectors.
So how can you measure neutrons in scrap metal and recycled metal?
Thermo Fisher Scientific has solved the problem of quickly identifying radiation sources in large shipments of scrap metal, by developing a new highly sensitive neutron detector module, which can be integrated into an existing Thermo Scientific gate monitor, or operated as a stand-alone installation. The truck simply drives through the gate monitor and is automatically scanned as it passes through.
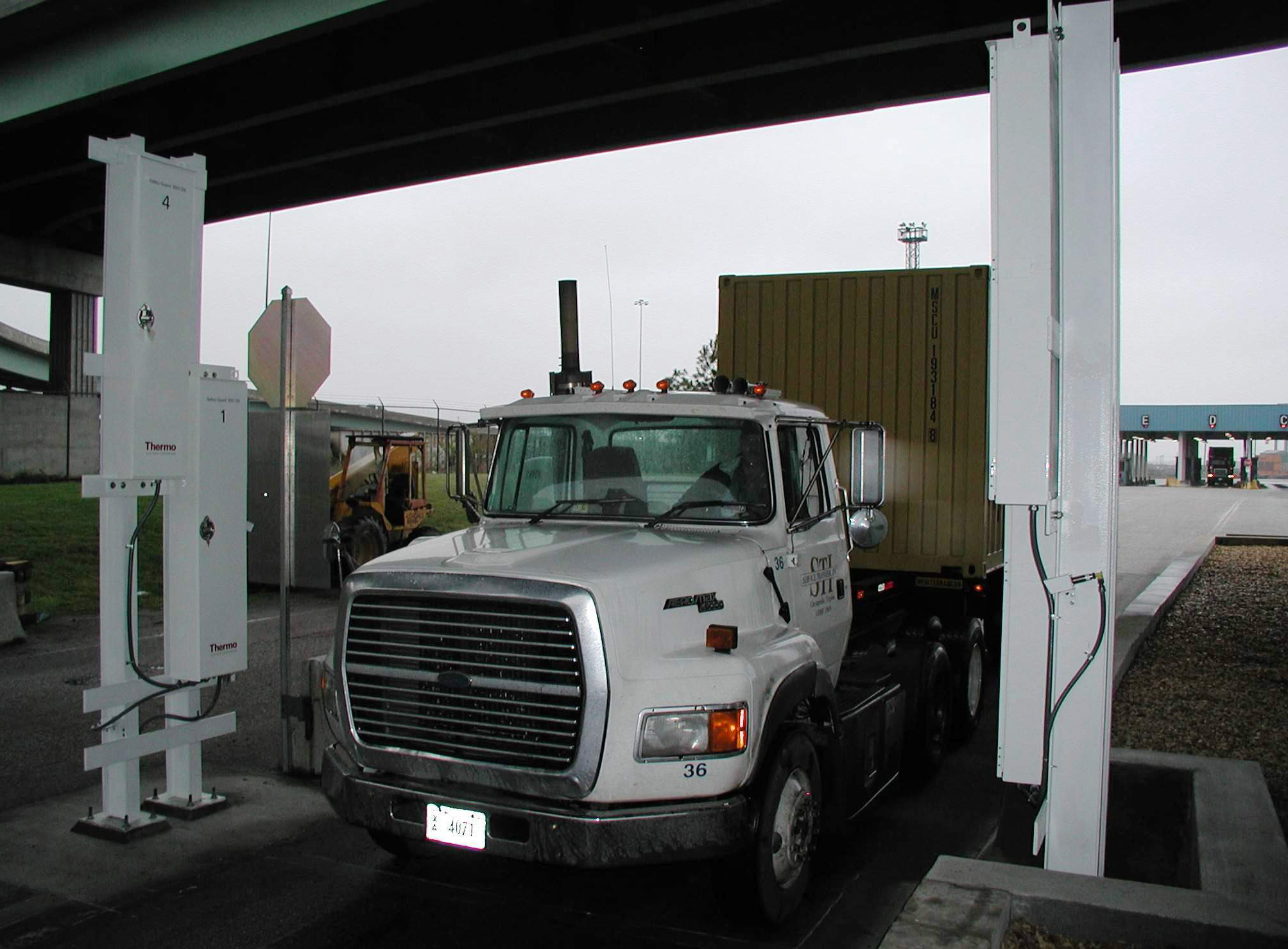

The detector operates by capturing thermal neutrons through the Li-6 (n,alpha) reaction. This produces intense scintillation pulses that are read out by a proprietary combination of bulk wavelength shifting waveguide, solid state photo multiplier and on-board electronics.
Compared to gamma radiation, these neutron particles are highly penetrating. Therefore, much less attenuated by the shielding of the source and the surrounding scrap metal.
In addition to the surprisingly good detection capability for high activity Am-241 sources, these systems also provide excellent protection against neutron sources (AmBe, Cf-252, Pu-238, Pu-240, Cm isotopes), which are commonly used in industry, including in low radiation activity portable devices which may be deeply buried in dense scrap material and remain undetected by conventional gate monitors.
The Thermo Scientific Neutron Gate Monitor FHT 1388S provides a high level of protection against the inadvertent melting of Americium radiation sources.
Features include:
- Modular monitor design for up to 8 dual neutron detectors
- Flat panel large area neutron detector elements embedded in thoroughly designed moderator and reflector housing for maximum sensitivity
- Optimized timing algorithm for best signal recognition and false alarm free operation
- Excellent source detection capabilities for industrial neutron and Am-241 sources (shielded and embedded in steel scrap) as low as - 1 - 5 mCi for AmBe (neutron gauge sources
- 200 - 1000 mCi for Am (gamma/X-ray gauges)
- Preferred location of monitor at stationary weighing bridge
- Stand-alone operation or integration into gamma portal monitor FHT 1388 S
- Easy installation - only 25 kg per detector module.
Thermo Fisher are currently offering the ASM IV gate monitor system at a promotional price. Customers looking to install the equipment in the near future should contact ADM Nuclear Technologies for the latest pricing information.
If you are concerned about detecting radiation in scrap metal, please don’t hesitate to contact ADM Nuclear Technologies. Our expert team will gladly answer any questions you may have.
IS THIS INFORMATION USEFUL?
If so, why not share it with your peers and colleagues. Simply click on the blue LinkedIn share icon below.




